Ledgers

Ledger is an accounting register, in which similar accounting transactions are recorded in summarized form.
In an Accounting Cycle, every transaction carried out by a business shall be documented upon a voucher. Then this transaction shall be recorded in a relevant journal in chronological order with specific details.
The detailed information of various transactions is to be further classified and summarizes so it can be processed for its intended use i.e. Reporting to Management and owners of the business.
Management and business owners may not need to see each and every transaction, however, they require information in summarize form to review performance and make decisions. For Example how much their business earned in a specific period (Total Sales in a period) or they might want to look at how much they owe to a particular supplier.
If we recall the definition of Accounting, it says that Accounting is the process of recording, summarizing, and reporting financial information. So posting information in ledgers is the second 2nd important part of the whole accounting process.
Ledgers are further divided into sub-ledgers, in fact, a Ledger may contain many sub-ledgers. For example, a General Ledger contains sub-ledgers of Salary, Purchase, Sales, and Assets, etc.
Ledgers are also named accounts, for example, salary ledger can also be termed as Salary accounts.
Sources of the data for the Ledger are Journals. The summary of the transactions is posted into the relevant sub-ledgers using the double-entry principle. It means if any amount is recorded on the Debit side of any ledger, the corresponding amounts must be recorded on the credit side of some relevant ledger. Ledgers are the 1st step in the accounting cycle to implement the double-entry accounting principle.
Information in the Ledger shall be recorded from Journal ONLY. Each entry in Ledgers shall be referred to the journal from which it was posted into the ledgers.

Types of Ledger
Due to the classification of the transactions, Ledgers can be classified into different types.
Personal Ledger
This ledger is used to maintain transactional records for persons and entities e.g. suppliers, customers, individuals, and organizations, etc. Payable and Receivable Ledger are the most common examples of personal ledger which contain personal sub-ledgers of each individual supplier and customer.
Personal Ledger can further be subdivided into the following three categories;
Natural Person Ledger
Ledger to maintain records of transactions with natural persons like individual Suppliers, and customers, etc.
Artificial Person Ledger
These are used to record transactional information of Artificial persons like companies, businesses, and organizations. Remember artificial persons are separate entities other than living human beings.
Representative of personal ledger
This type of Ledger contain accounting information in relation to a group of persons (natural/ artificial). For example salary payable account, accrued interest ledger, and prepaid insurance expense, etc.
Sales Ledger Control Account also termed and Receivable Ledger Control Account and similarly Purchase Ledger Control Account also termed and Payable Ledger Control Account are two widely used ledgers, which can be termed
Impersonal Ledger
Any ledger other than the personal ledgers described above is called an impersonal ledger. For example ledgers for assets, liabilities, and expenses, etc.
Impersonal ledger are further divided into the following two categories;
Nominal Ledger
Nominal ledger is maintained to keep the record for those accounts which will be closed and be part of Profit and Loss for a period. Examples of Nominal Ledger are Purchase, Sales, salary and interest expense, etc. accounts.
Real Ledger
Real Ledgers represents those accounts, balances of which are carried forwarded at any period end. These accounts become part of balance sheets. Examples include assets, liabilities, and Capital accounts. Real Ledgers can further be classified into tangible and Intangible Ledger.
Tangible Real Ledger
Ledger maintained for those accounts which can be physically touched like assets compute, Plant and Machinery, Cars, etc.
Intangible Real Ledger
Ledger maintained for intangible assets e.g. Software, copyrights, etc. are called intangible ledgers.
Manual Ledger are also called T-Accounts
The ledger is also mentioned as T account in day to day language. This is because if you have noticed the shape of the ledger you might have noticed it looked like the word “T”.
The title of the ledger/ account at the top of the page represent the horizontal line of the word T,
whereas the line separating the debit and credit side of the account can be denoted at the vertical line of the word T.
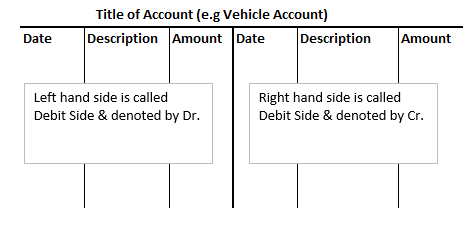
Note: It is not mandatory to always follow the same format, as in computerized environments, there are 3 columns used as debit, credit, and balance. After each entry in the ledger, the Balance column is updated. However, This real-time balancing of accounts is not possible in manual bookkeeping.